RBM tracks the water balance of a water source
Water demands and available water (for use) are regularly checked and updated for all monitored water sources.
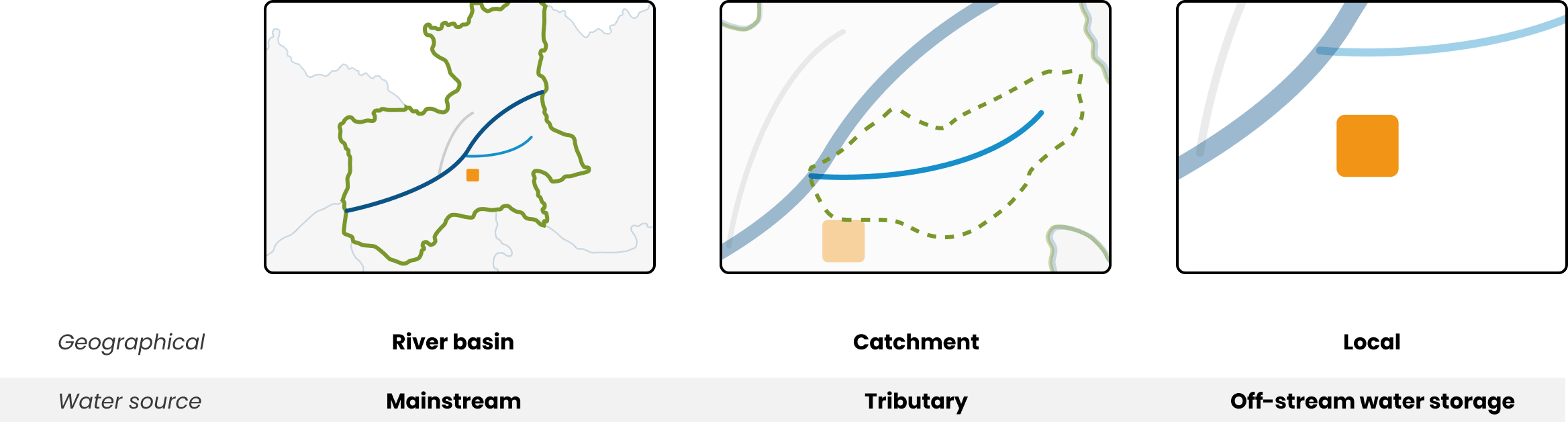
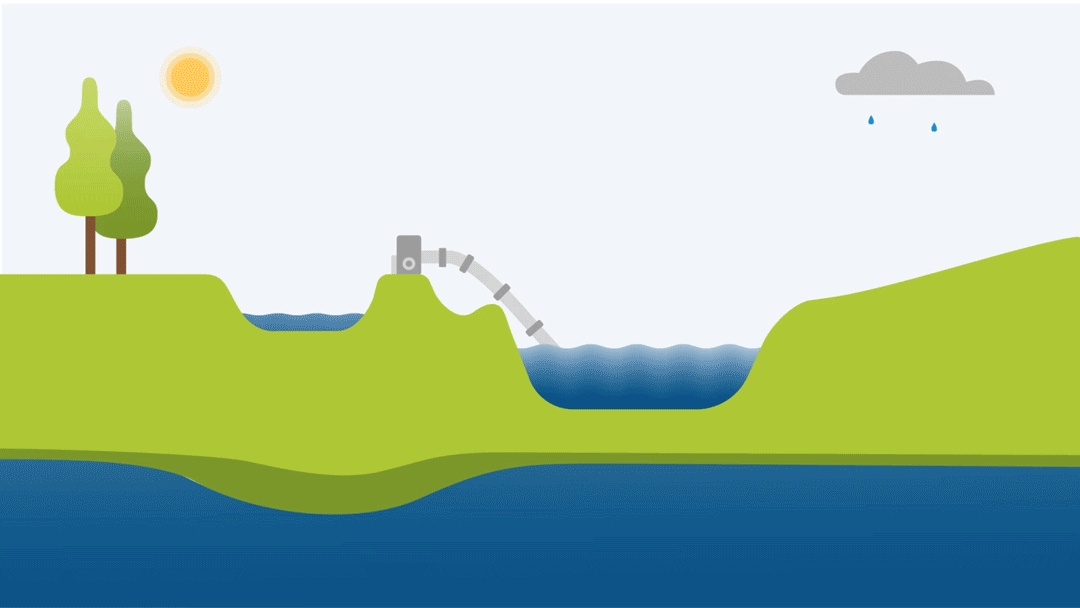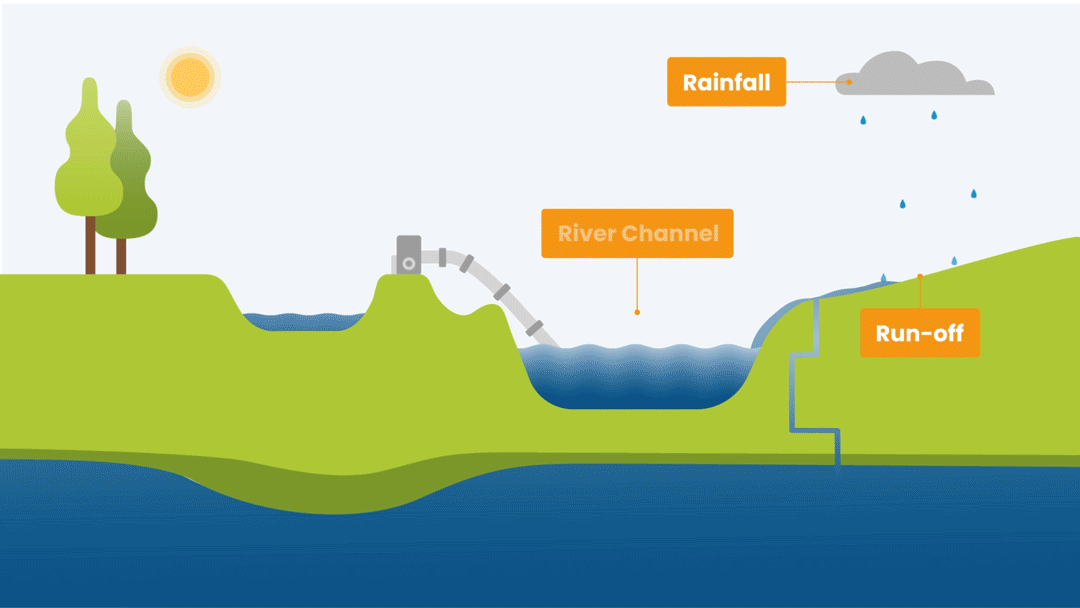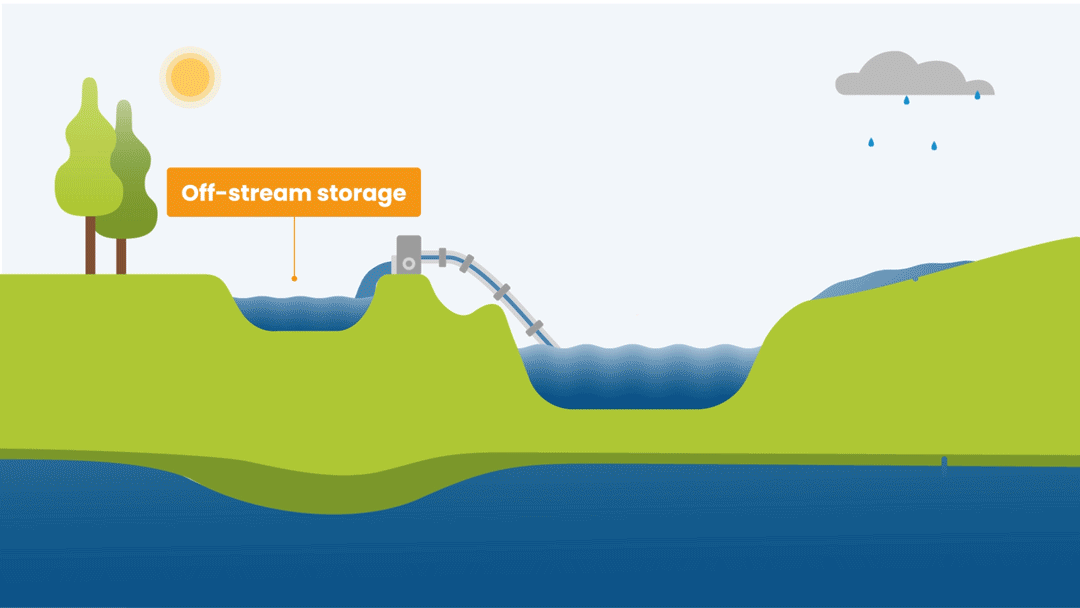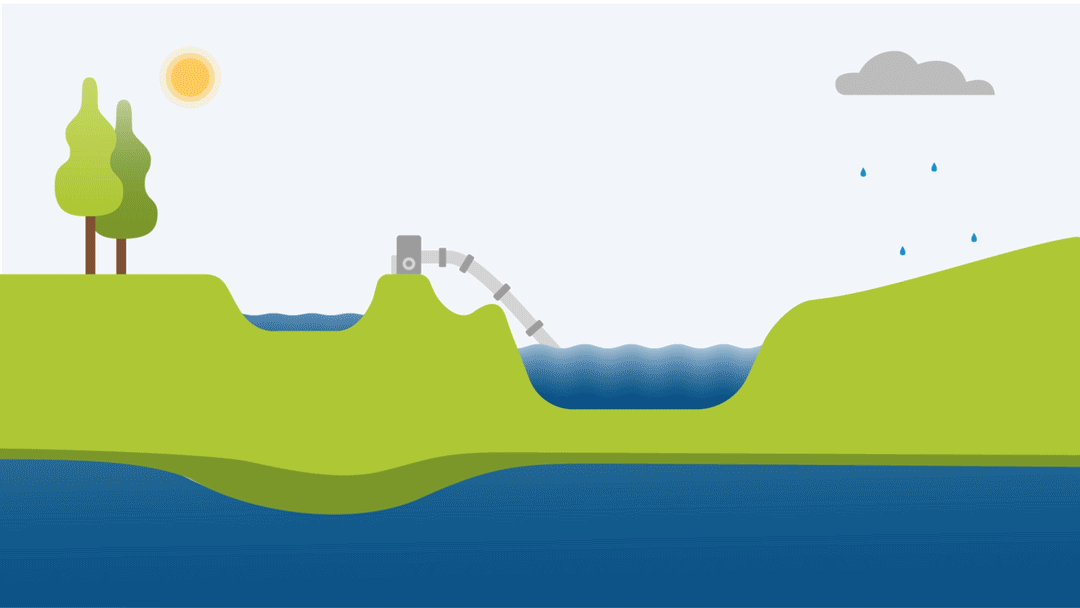
Water Source
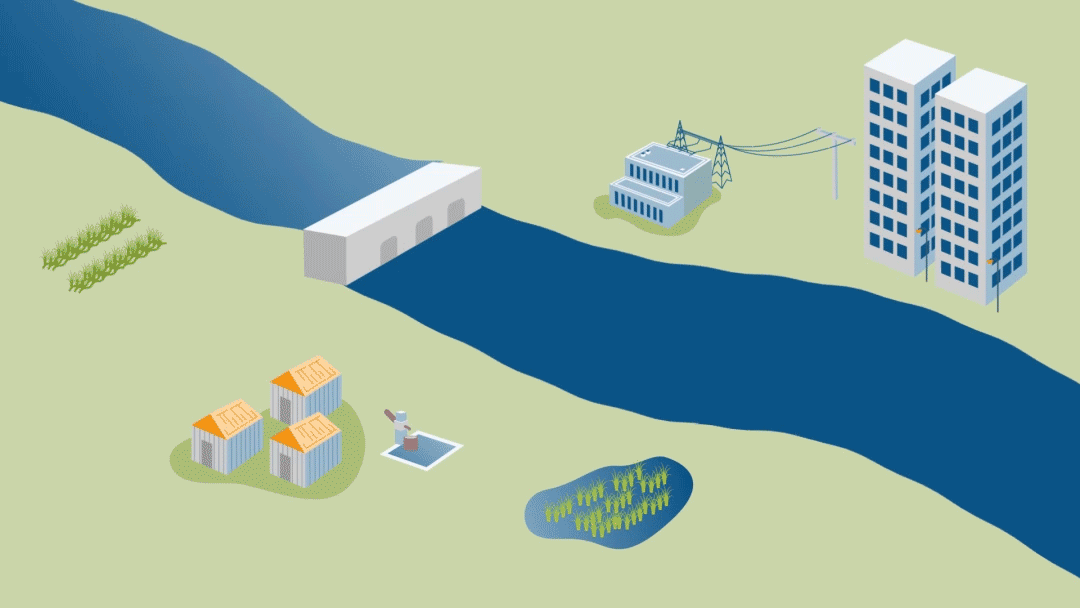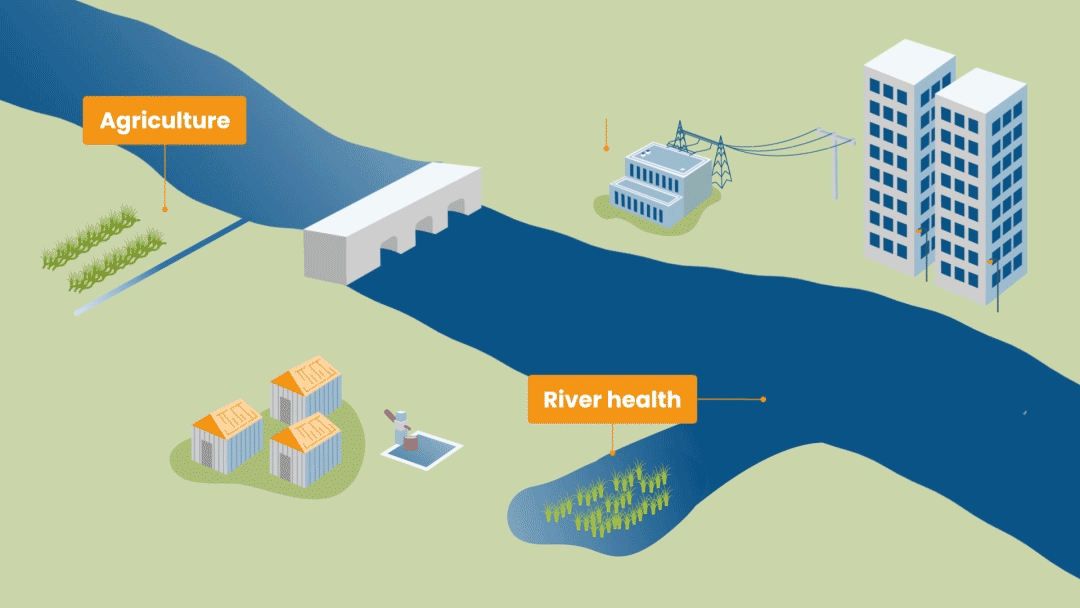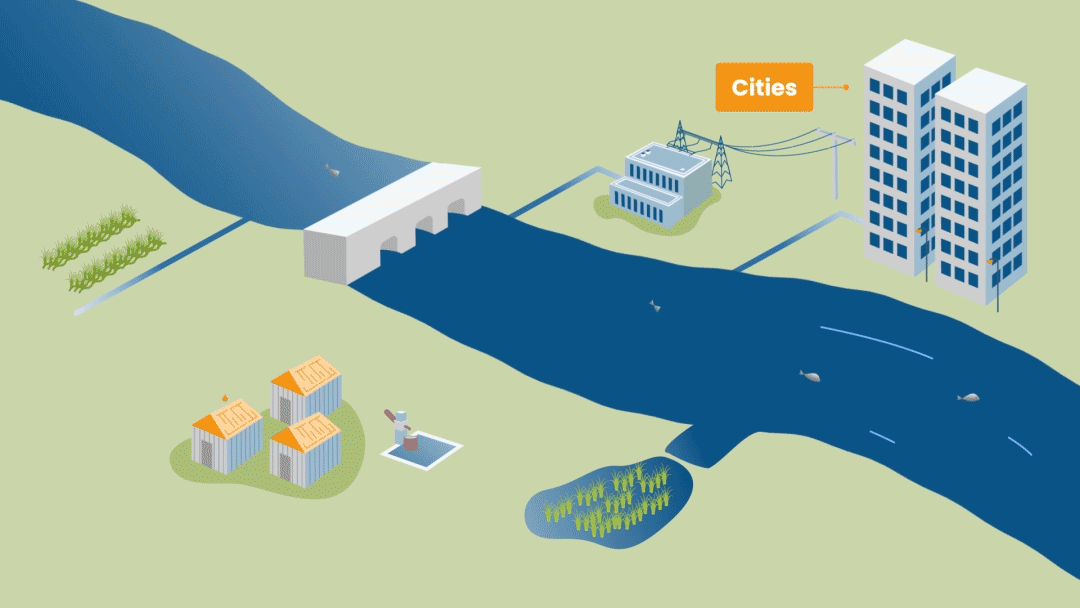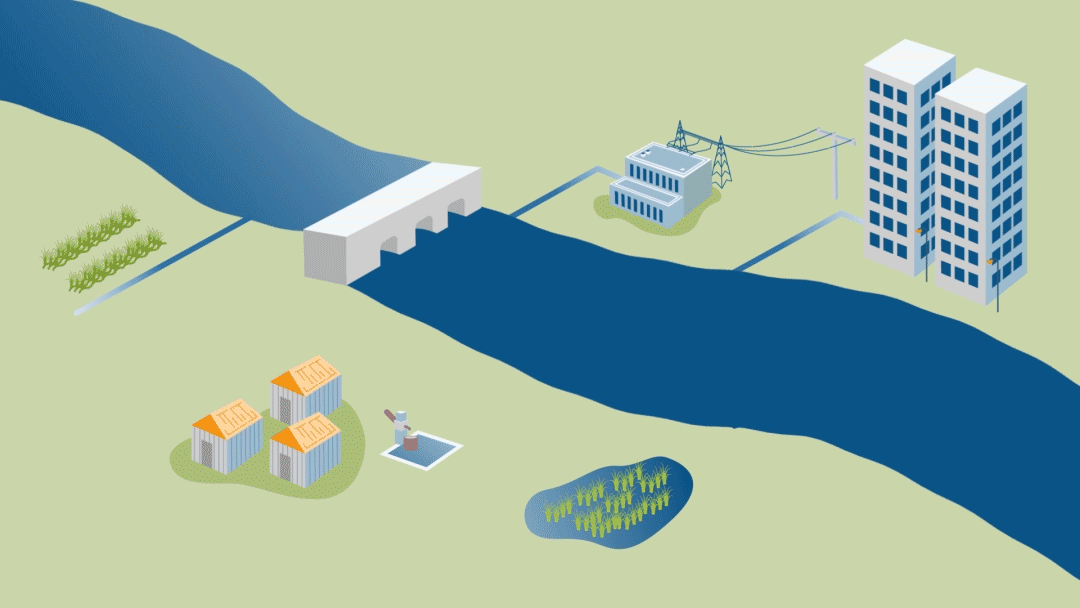
Reservoirs, off-stream water storages, aquifers, rainfall are all types of water sources. A hydropower company will use water in a river to generate electricity whereas a farmer could use multiple water sources, pumping water from a river or an aquifer as well as using rainfall to grow crops.
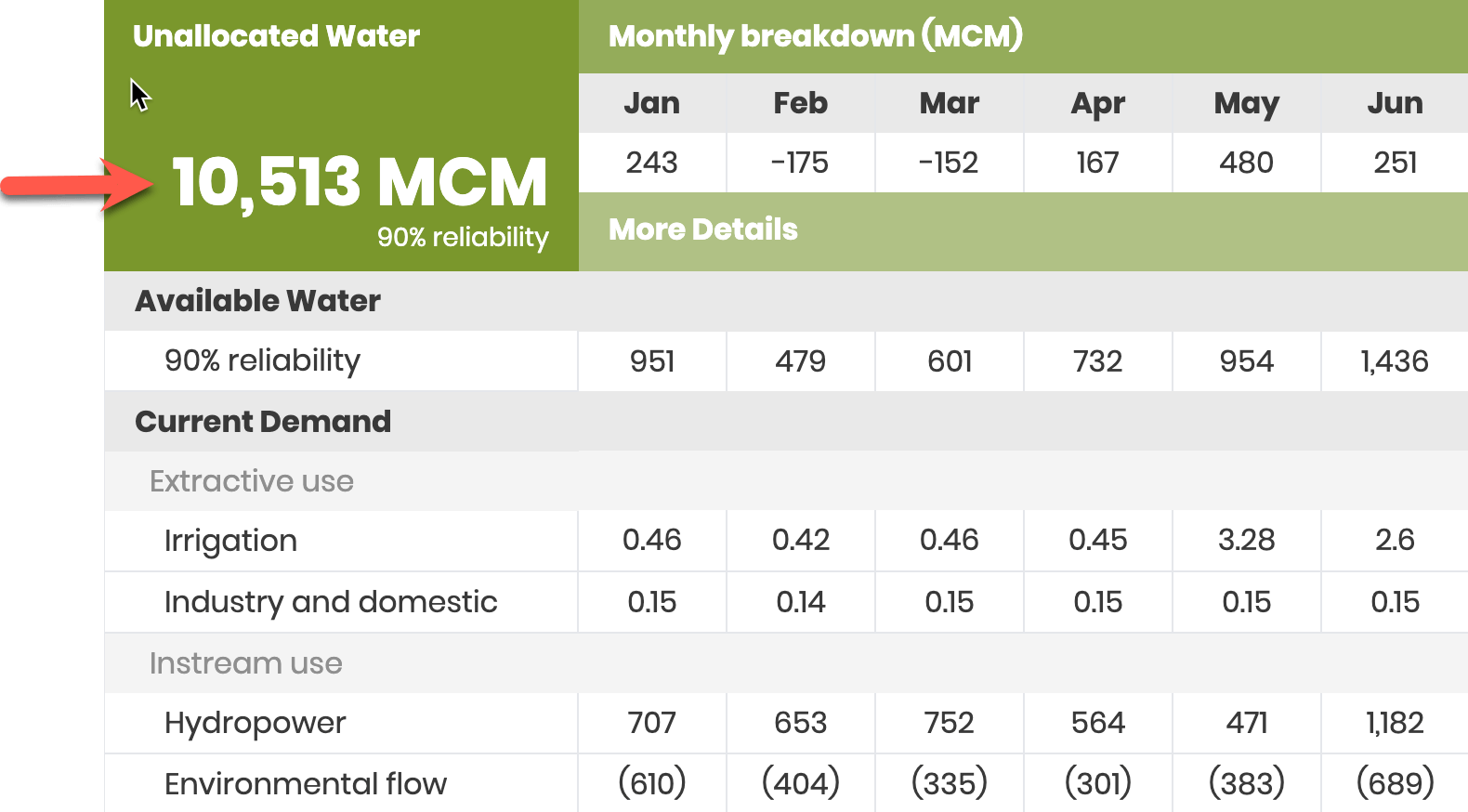
Available Water
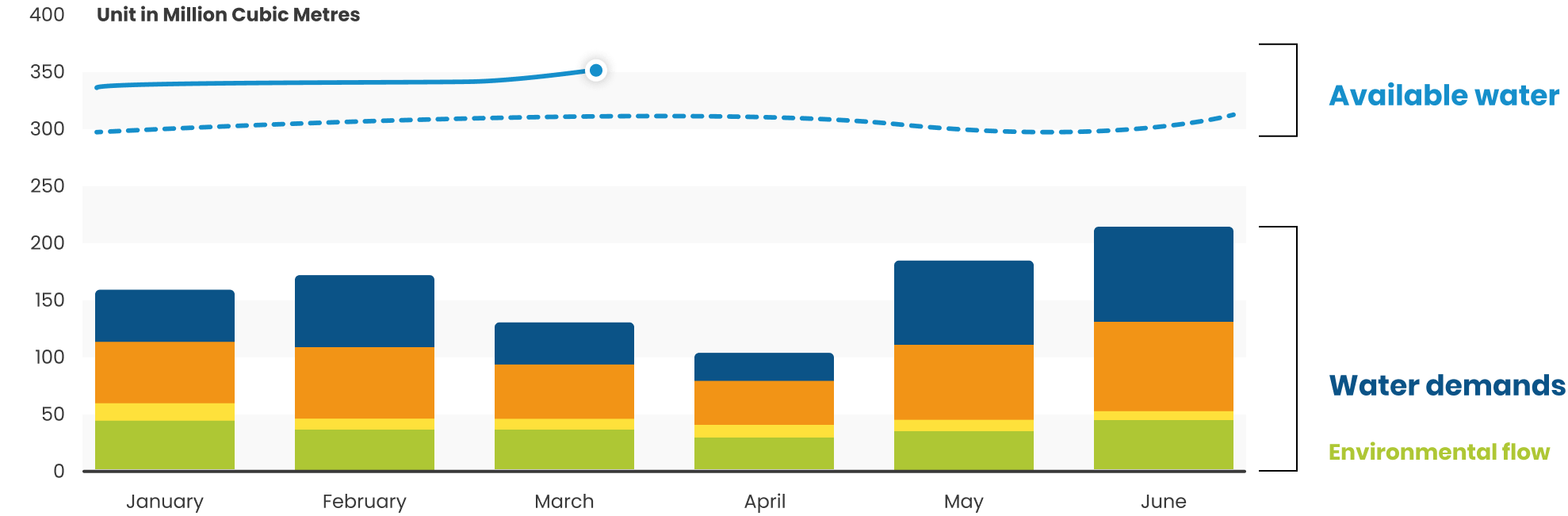
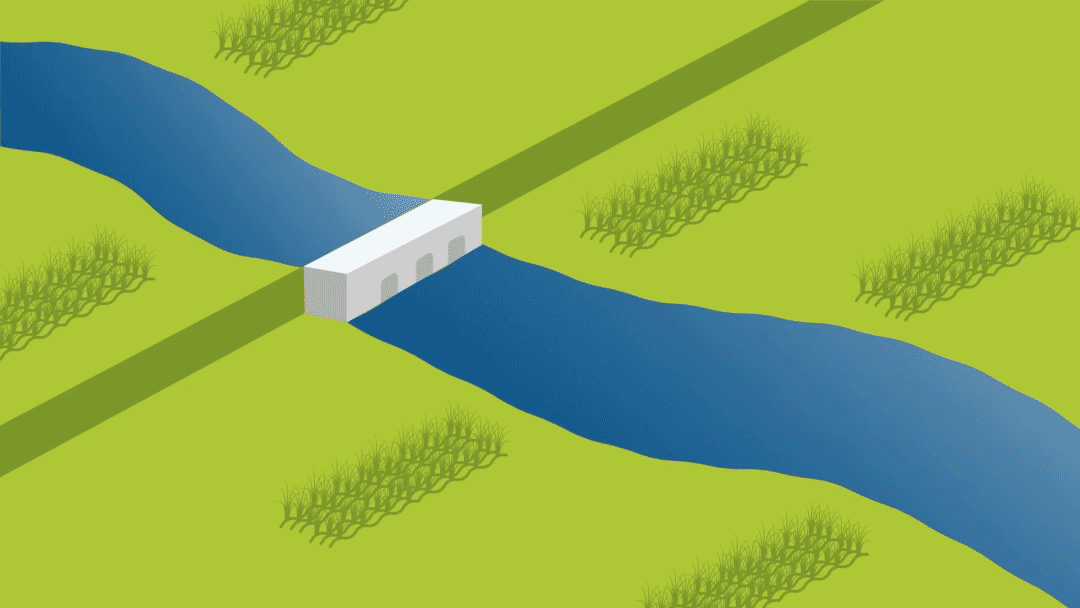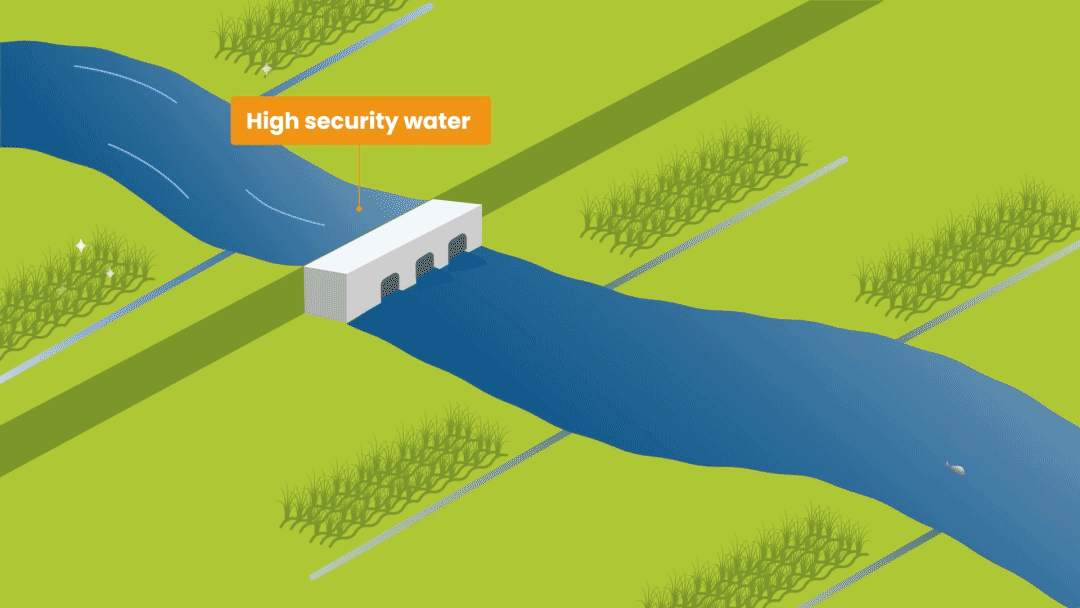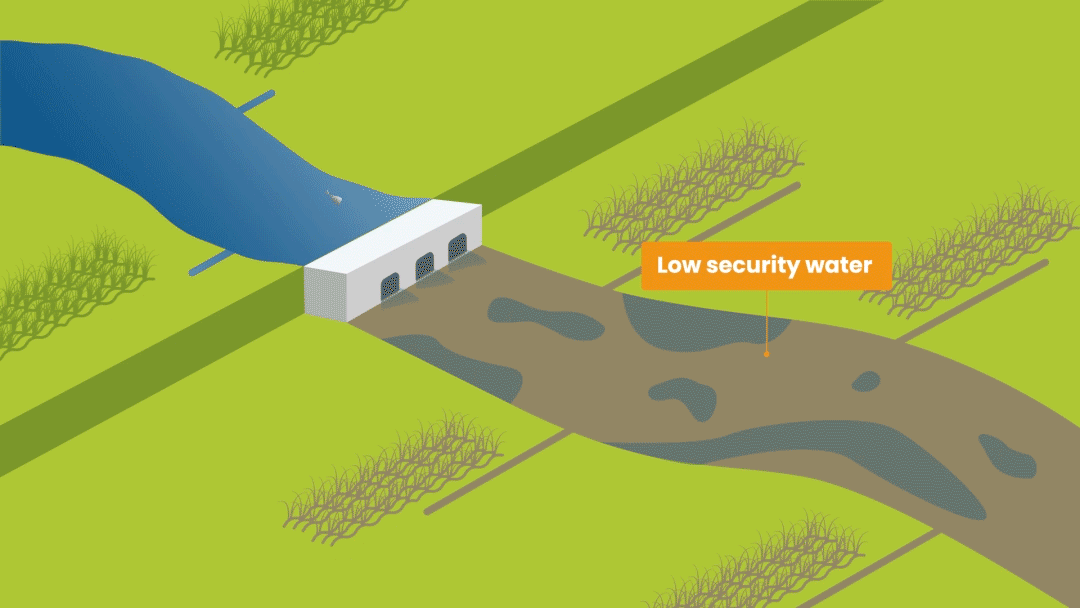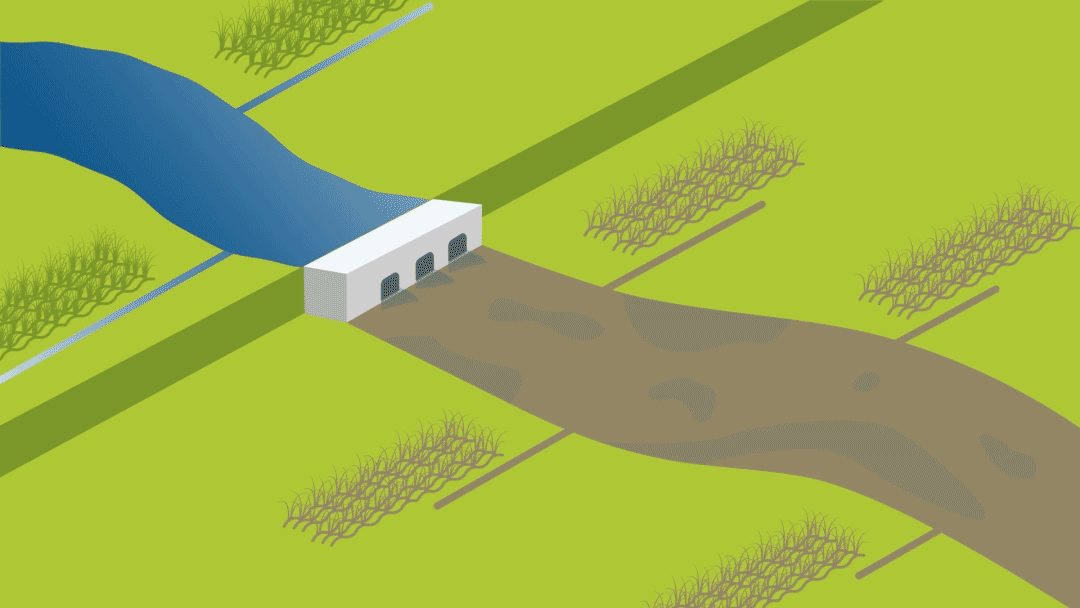
This is the volume of water available for use in a water source over a period. A water balance simulation model is used to weigh up the water coming in and out of the water source, including water losses from evaporation and infiltration, to calculate how much water is available. RBM tracks two metrics: (1) high security (reliability of 90%+) water and (2) current available water where there is automatic water level monitoring data available. The high security metric is used for calculating the water balance to give confidence to users that the water they need is available in 9 out of 10 years.
Water Demands
RBM tracks both extractive - irrigated agriculture, industry and domestic use - and in-stream - hydropower and environment flow - water demands. Satellite data, graphs and tables are used to show the location of water users and the water demand at the sector level. Different user access levels can be set up to protect commercially and other sensitive information.
Environmental flows is the water required for protecting river health. These flows are different to a baseline or a minimum flow as they are designed to help trigger ecological responses in a river.
Water Balance
Shows the difference between the available water at 90% reliability and the water demands over different time scales (annual, seasonal, and monthly). Unallocated water is the volume of water that can be safely used without impacting existing users water requirements